A week is a unit of time equal to seven days. It is the standard time period used for short cycles of days in most parts of the world. The days are often used to indicate common work days and rest days, as well as days of worship. Weeks are often mapped against yearly calendars, but are typically not the basis for them, as weeks are not based on astronomy.
The modern seven-day week can be traced back to the Babylonians, who used it within their calendar. Other ancient cultures had different week lengths, including ten in Egypt and an eight-day week for Etruscans. The Etruscan week was adopted by the Ancient Romans, but they later moved to a seven-day week, which had spread across Western Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean. In 321 AD, Emperor Constantine officially decreed a seven-day week in the Roman Empire, including making Sunday a public holiday. This later spread across Europe, then the rest of the world.
In English, the names of the days of the week are Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, and Sunday. In many languages, the days of the week are named after gods or planets visible to the eye. Such a week may be called a planetary week. Certain weeks within a year may be designated for a particular purpose, such as Holy Week in Christianity, Golden Week in China, and National Family Week in Canada. More informally, certain groups may advocate awareness weeks, which are designed to draw attention to a certain subject or cause. The term “week” may also be used to refer to a sub-section of the week, such as the workweek and weekend.
Cultures vary in which days of the week are designated the first and the last, though virtually all have Saturday, Sunday or Monday as the first day. The Geneva-based ISO standards organization uses Monday as the first day of the week in its ISO week date system through the international ISO 8601 standard. Most of Europe and China consider Monday the first day of the week, most of North America and South Asia consider Sunday the first day, while Saturday is judged as the first day of the week in much of the Middle East and North Africa. Other regions are mixed, but typically observe either Sunday or Monday as the first day. The Jewish week ends with nightfall on Saturday, at the conclusion of the Sabbath, following the Hebrew Bible in which God created the world in six days and rested on the seventh. Most Christians set their Sabbath to Sunday, so as not to coincide with Judaism[citation needed]. Muslims set their Sabbath to Friday because it was described as a sacred day of worship in the Quran.
Name
The English word week comes from the Old English wice, ultimately from a Common Germanic *wikōn-, from a root *wik- “turn, move, change”. The Germanic word probably had a wider meaning prior to the adoption of the Roman calendar, perhaps “succession series”, as suggested by Gothic wikō translating taxis “order” in Luke 1:8.
The seven-day week is named in many languages by a word derived from “seven”. The archaism sennight (“seven-night”) preserves the old Germanic practice of reckoning time by nights, as in the more common fortnight (“fourteen-night”). Hebdomad and hebdomadal week both derive from the Greek hebdomás (ἑβδομάς, “a seven”). Septimana is cognate with the Romance terms derived from Latin septimana (“seven mornings”).
Slavic has a formation *tъ(žь)dьnь (Serbian тједан, tjedan, Croatian tjedan, Ukrainian тиждень, tyzhden, Czech týden, Polish tydzień), from *tъ “this” + *dьnь “day”. Chinese has 星期, as it were “planetary time unit”. An older Chinese form is 禮拜, meaning “week, religious ceremony.”
Definition and duration
A week is defined as an interval of exactly seven days,so that, except when passing through daylight saving time transitions or leap seconds,
1 week = 7 days = 168 hours = 10,080 minutes = 604,800 seconds.
With respect to the Gregorian calendar:
- 1 Gregorian calendar year = 52 weeks + 1 day (2 days in a leap year)
- 1 week = 1600⁄6957 ≈ 22.9984% of an average Gregorian month
In a Gregorian mean year, there are 365.2425 days, and thus exactly 52+71⁄400 or 52.1775 weeks (unlike the Julian year of 365.25 days or 52+5⁄28 ≈ 52.1786 weeks, which cannot be represented by a finite decimal expansion). There are exactly 20,871 weeks in 400 Gregorian years, so 29 November 1623 was a Wednesday just as was 29 November 2023.
Relative to the path of the Moon, a week is 23.659% of an average lunation or 94.637% of an average quarter lunation.
Historically, the system of dominical letters (letters A to G identifying the weekday of the first day of a given year) has been used to facilitate calculation of the day of week. The day of the week can be easily calculated given a date’s Julian day number (JD, i.e. the integer value at noon UT): Adding one to the remainder after dividing the Julian day number by seven (JD modulo 7 + 1) yields that date’s ISO 8601 day of the week. For example, the Julian day number of 29 November 2023 is 2460278. Calculating 2460278 mod 7 + 1 yields 3, corresponding to Wednesday. In 1973, John Conway devised the Doomsday rule for mental calculation of the weekday of any date in any year.
Days of the week
Main article: Names of the days of the week
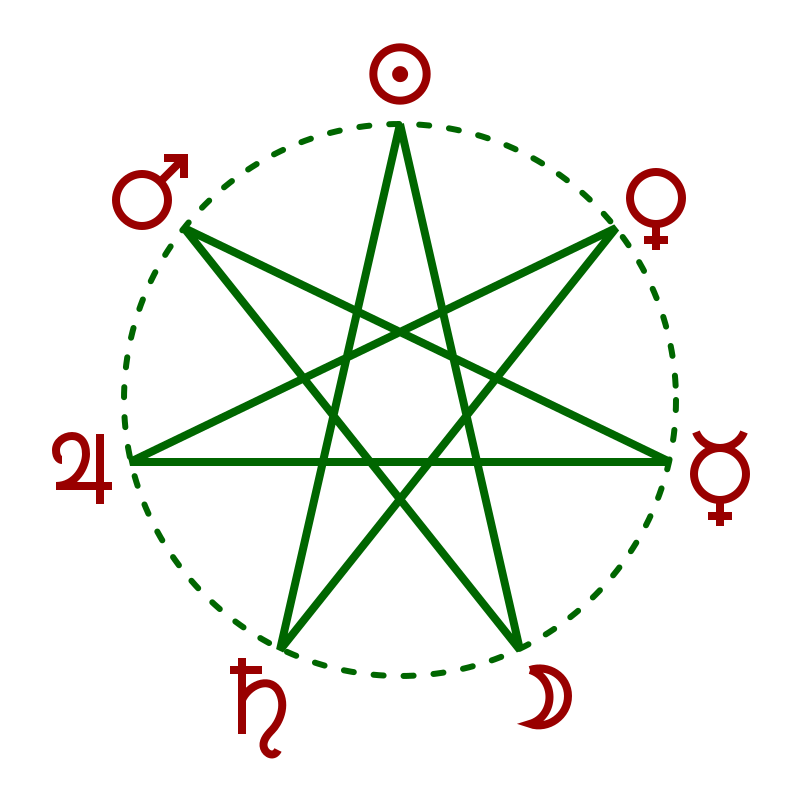
The days of the week were named for the classical planets. This naming system persisted alongside an “ecclesiastical” tradition of numbering the days in ecclesiastical Latin beginning with Dominica (the Lord’s Day) as the first day. The Greco-Roman gods associated with the classical planets were rendered in their interpretatio germanica at some point during the late Roman Empire, yielding the Germanic tradition of names based on indigenous deities.
The ordering of the weekday names is not the classical order of the planets (by distance in the planetary spheres model, nor, equivalently, by their apparent speed of movement in the night sky). Instead, the planetary hours systems resulted in succeeding days being named for planets that are three places apart in their traditional listing. This characteristic was apparently discussed in Plutarch in a treatise written in c. 100 CE, which is reported to have addressed the question of Why are the days named after the planets reckoned in a different order from the actual order? (the text of Plutarch’s treatise has been lost).













Reviews
There are no reviews yet